
by Maria Ibarra Rodriguez, intern, global program management, ICMA
The quality of life in cities across the nation is underpinned by health-related efforts, such as health surveillance, child health services, and other initiatives to create healthier, thriving communities. Healthier communities are more likely to recruit and retain businesses, develop the local labor force, and attract external investment to enhance economic growth.
To help cities build healthier, more equitable communities, the City Health Dashboard (CHDB) was created with support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation to support health-related decision making in cities.
Recently, the Smart Growth Network hosted a webinar on how social, environmental, and economic factors that drive health and sustainability are challenging local communities. The webinar gave a demonstration of the CHDB, along with firsthand local government insight on how using the CHDB can enhance data-driven policymaking. Below are some of the main takeaways from the webinar.
A One-Stop Resource
CHDB is a one-stop resource that centralizes comprehensive data from federal, state, and other datasets on health and social determinants of health. CHDB can be accessed by cities to understand how they are performing on health outcomes and to help them make informed health-related decisions. The data is provided at a city and census tract level on 37 measures of health across five categories: social and economic factors, physical environment, health behavior, health outcomes, and clinical care. While the data can be downloaded for further analysis by someone in a city government office, CHDB can also generate a dashboard of data visualizations and make comparisons across cities or metrics to make better sense of the data by simply selecting a few options. This can be an advantage for cities that have a limited data capacity, but still want to determine how they can generate better health outcomes in their communities.
Helping Cities Enhance Decision Making
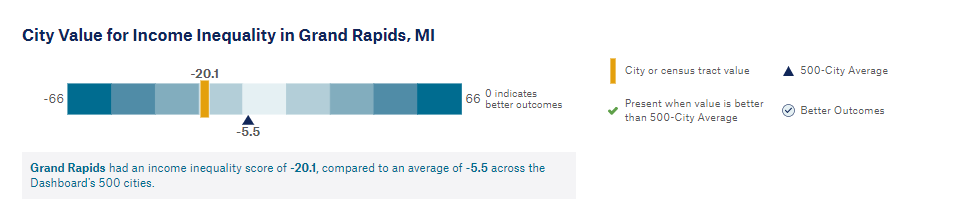
After the launch of CHDB in May 2018, the city of Grand Rapids, Michigan, saw CHDB as an opportunity to obtain data that the city needed to enhance decision making that was previously not easily accessible. Prior to using CHDB, the city was making decisions based on resident interaction and census data. Today, the city uses CHDB daily to enhance its decision making by downloading data from CHDB and correlating it with its databases to better understand the needs of their residents. Becky Jo Glover of Grand Rapids noted that when the city was basing decision making on resident interactions, the city was not effectively reaching low-to-moderate income (LMI) households with policies that had them travel longer distances during the hours of 8 am to 5 pm to go to the 311 office and pay their bills. This created an unnecessary barrier for LMI residents that had to take time off from work and travel long distances, negatively impacting their income.
Using CHDB, the city was able to address this issue by creating a “digital city hall” for residents to make their payments online, making the payment process more accessible to all residents. In the past eight months, there has been a significant drop in customers visiting the physical office, as most of bill payment interactions occur online saving residents time and money. The city is constantly using CHDB to identify areas where they can be delivering better services to residents by engaging in better decision making to create a healthier community. Additionally, Glover mentioned that because of the wealth of data in CHDB, they have been able to develop partnerships across sectors, such as the health insurance sector, academia, and others, to proactively address community needs and make informed policy decisions for the community.
An Amenable and Helpful Tool
CHDB is a flexible tool that can be used by any city to see how it is performing and find information on how to act on it. By using CHDB you will be able to:
- Access and visualize data on different health metrics and social determinants of health in your city.
- Make data comparisons across cities or metrics.
- Download datasets that are of interest to the city for further analysis.
- Learn how your city can take action.
CHDB is updated regularly and will soon host additional data sources, provide health-related data for small cities, and include additional breakdowns to help cities make more informed health-related decisions.
Missed the webinar? You can view the recording and access the presenter slides here.
New, Reduced Membership Dues
A new, reduced dues rate is available for CAOs/ACAOs, along with additional discounts for those in smaller communities, has been implemented. Learn more and be sure to join or renew today!
